Examples¶
The following examples PEGS used in different analyses:
Mouse glucocorticoidal dataset¶
Thanks to Louise Hunter for providing this example.
Note
The input files and the resulting outputs can be obtained by
downloading and unpacking the tar.gz archive at
glucocorticoid_example.tar.gz
Background¶
An example application of PEGS is the analysis of up- and
down-regulated glucocorticoidal targets from an RNA-seq study
of liver samples from mice treated acutely with dexamethasone
or vehicle (Caratti et al. 2018), combined with corresponding
GR ChIP-seq and chromatin accessibility data (DNase I
hypersensitive (DHS) regions) (Grontved et al. 2013 and
Sobel et al. 2017 respectively), and mouse liver TAD
boundary data (Kim et al. 2018).
The files for these datasets are:
RNA-seq data:
1_zt6up.txtand2_zt6down.txt(placed in aclustersdirctory)ChIP-seq and chromatin accessibility data:
Grontved_GR_ChIP.bedandZT6_DNase.bed(placed in apeaksdirectory)TAD boundary data:
mESC-TADs_mm10.txt
PEGS analysis¶
PEGS can be run on these data using the command:
pegs mm10 \
--peaks data/peaks/*.bed --genes data/clusters/*.txt \
-d 1000 5000 10000 50000 100000 200000 500000 1000000 5000000 \
--tads data/mESC-TADs_mm10.txt \
--name glucocorticoid \
-o results/
This outputs a PNG heatmap
glucocorticoid_heatmap.png:
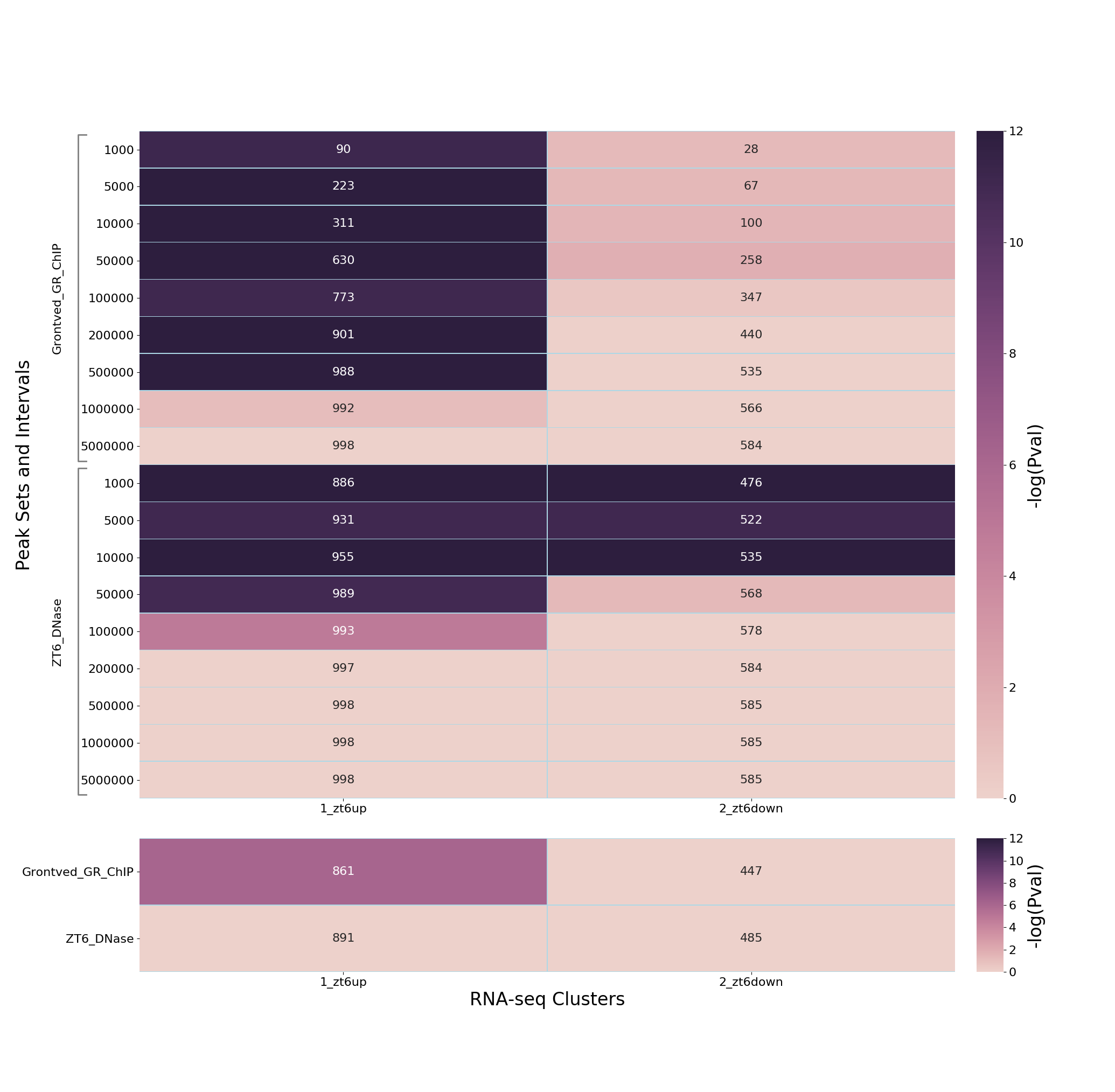
along with an XLSX file that contains the raw data
glucocorticoid_results.xlsx.
Conclusions¶
The analyses indicate a strong association of dexamethasone up-regulated genes with dexamethasone-induced GR peaks at distances up to 500kbp from these peaks, but no evidence of down-regulated genes - indicating distinct mechanisms of gene activation and repression by glucocorticoids. At the same time, there is promoter proximal enrichment for both up-and down-regulated genes in the DHSs.
References¶
Caratti, G. et al. (2018) REVERBa couples the clock to hepatic glucocorticoid action. J Clin Invest 128(10):4454-4471
Grontved, L. et al. (2013) C/EBP maintains chromatin accessibility in liver and facilitates glucocorticoid receptor recruitment to steroid response elements. EMBO J 32(11), 1568-83
Kim, Y.H. et al. (2018) Rev-erbα dynamically modulates chromatin looping to control circadian gene transcription. Science 359(6381):1274-1277
Sobel, J.A. et al. (2017) Transcriptional regulatory logic of the diurnal cycle in the mouse liver. PLoS Biol 15(4): e2001069